Document Structure

DOM Structure
- the DOM follows the same structure
- objects inside of objects, inside of objects
- we can interact with these objects to:
- get information
- add or change information
- add events
- global variable
documentcontains the DOM
Trees
- this data structure is called a tree
- there are nodes for elements
- represent HTML tags
- determine the structure
- can have children
- other elements
- leaf nodes such as text content, comments, etc.
Trees (continued)
- each node object has a
nodeType- elements nodes are
1 - JS has constants such as
document.ELEMENT_NODEto make this easier
- elements nodes are
Trees (continued)

Finding Elements
- we can find element directly
document.getElementsByTagName("a")document.getElementsByClassName("selected")- these return an array like object called an HTMLCollection
document.getElementById("gertrude")- returns a single element
Finding Elements - New Way
-
new methods in JavaScript (IE9+) make selecting elements even easier
-
use CSS selectors to select elements
-
with these two, you don't need any of the previous methods
document.querySelector()- returns the first matching elementdocument.querySelectorAll()- returns an array like object, a NodeList, of all matching elements
Static vs Live
- some methods return live lists that will update if the DOM changes
.getElementsByTagName()and.getElementsByClassName()return a live list- it will be updated if the DOM changes
.querySelectorAll()returns a static list- it will not change as elements are added or removed
Converting to an Array
Array.from()is a new method for making an array from an array like object- not supported in Internet Explorer
- Simplest form, just takes one argument:
let arrayish = { 0: 'one', 1: 'two', length: 2 };
let array = Array.from(arrayish);
Moving Through the Tree
- nodes have properties for moving around the tree
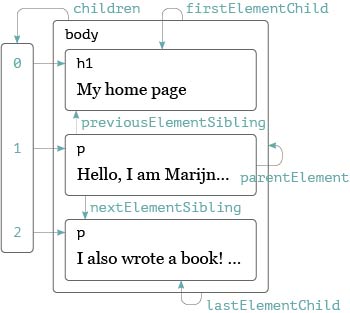
These are different than the textbook but only select elements, skipping other nodes.
.children.firstElementChild.lastElementChild.nextElementSibling.previousElementSibling.parentElement
Changing the Document
- almost everything in the DOM can be changed
- some methods:
.remove().replaceWith().appendChild().insertBefore()
Working with Content
To make it easier to work with the content of elements we have two properties:
.textContent- only gets or sets text content of the element.innerHTML- contained elements are represented as tags
Creating Nodes
- can create new text and element nodes
document.createElement()document.createTextNode()
Attributes
- most common attributes can be accessed as properties of the DOM element
- eg.
hrefis.href,idis.id
- eg.
- others accessed through methods:
getAttribute()setAttribute()
- if you create your own attributes, prefix with
data-
class Attribute
classis a reserved word in JavaScript- use the property name
classNameinstead - browsers also have an array like property
classList- has methods for dealing with classes
.add(),.remove(),.toggle(),.contains()
- has methods for dealing with classes
Styling
styleproperty contains properties for every possible style
const para = document.getElementById('para');
console.log(para.style.color);
para.style.color = 'magenta';
- some style names contain dashes
- use camel case instead:
font-familybecomesfontFamily
Cascading Styles
- the
styleproperty applies directly to the element - it has the highest precedence
- will over-rule stylesheets or inherited styles
Summary
- JavaScript programs can inspect and change the page
- the data structure of the page is called the DOM and is accessed by the variable
document - the DOM is organized like a tree
- we can select, read, and modify element and text in the DOM
- styles can influence the way elements are displayed